Table of contents
- WHAT IS A BLOCK?
- Contents in a BLOCK :
- Block Number : Block Number is better known as BLOCK HEIGHT . The number represents how many blocks precede the current block in the network.
- Hash of the Previous Block : Hashing , in layman terms, means converting some entity (text, image, document, message etc.) into a string of characters of fixed length (ex : 057fe5c96ab). There are 16 options to choose from for each character. Hashing helps in reducing the size of the entity and making it secure as decrypting a hash is nearly impossible (along with other security techniques in blockchain).
- Timestamp : Timestamp indicates the time and date when the block was mined (included in the blockchain after validation).
- Nonce : Nonce is basically a randomly generated number of size 4 bytes.
- Merkle Root : Merkle Root is the topic I will be covering in a separate blog but in basic language its the resultant hash of the hashing algorithm applied on all the data in a block. So, you can understand it as the hash of the current block.
Hello Blockchain enthusiasts!! 👋👋
I am back with some more content on BLOCKCHAIN FUNDAMENTALS in continuation of my previous blog where I explained, at the very basic level, the idea behind blockchain, decentralization and distribution (Check it out here if you haven't : tanisi11.hashnode.dev/wtf-is-blockchain-dec.. )
Jumping on to today's topic :
WHAT IS A BLOCK?
A block is the most fundamental part of a blockchain. They can be called as the building blocks of a blockchain. All the transactions taking place in a blockchain are recorded in these blocks. Usually a Bitcoin block can record 1500-2000 transactions in order to avoid traffic congestion. But this number can vary on different blockchains. The size of a typical Bitcoin block is limited to 1MB. Whereas if we talk about Ethereum, the size of the block is not fixed. It depends on Gas limit. Each block has a gas limit (think of gas as a unit like kg/m/cm) which is determined by the complexity of contracts (in simple terms : codes) it has to run.
Let's say the gas limit is 15,000,000 and the minimum gas on a transaction is 21,000, hence the number of transactions that block can hold will be :
15,000,000 gas limit / 21,000 gas per transaction = 710 transactions (approx.)
But this number (710) is never reached as there are transactions with higher gas than 21000 ( DO NOT confuse gas with gas price. They are different concepts altogether.) . As the gas per transaction increases, the number of transactions a block can include decreases.
Contents in a BLOCK :
The below image shows the basic information a block has :
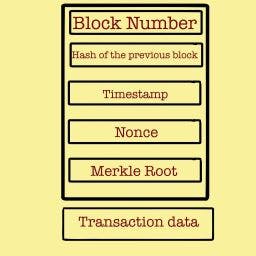
Let's know them one by one :
Block Number : Block Number is better known as BLOCK HEIGHT . The number represents how many blocks precede the current block in the network.
Hash of the Previous Block : Hashing , in layman terms, means converting some entity (text, image, document, message etc.) into a string of characters of fixed length (ex : 057fe5c96ab). There are 16 options to choose from for each character. Hashing helps in reducing the size of the entity and making it secure as decrypting a hash is nearly impossible (along with other security techniques in blockchain).
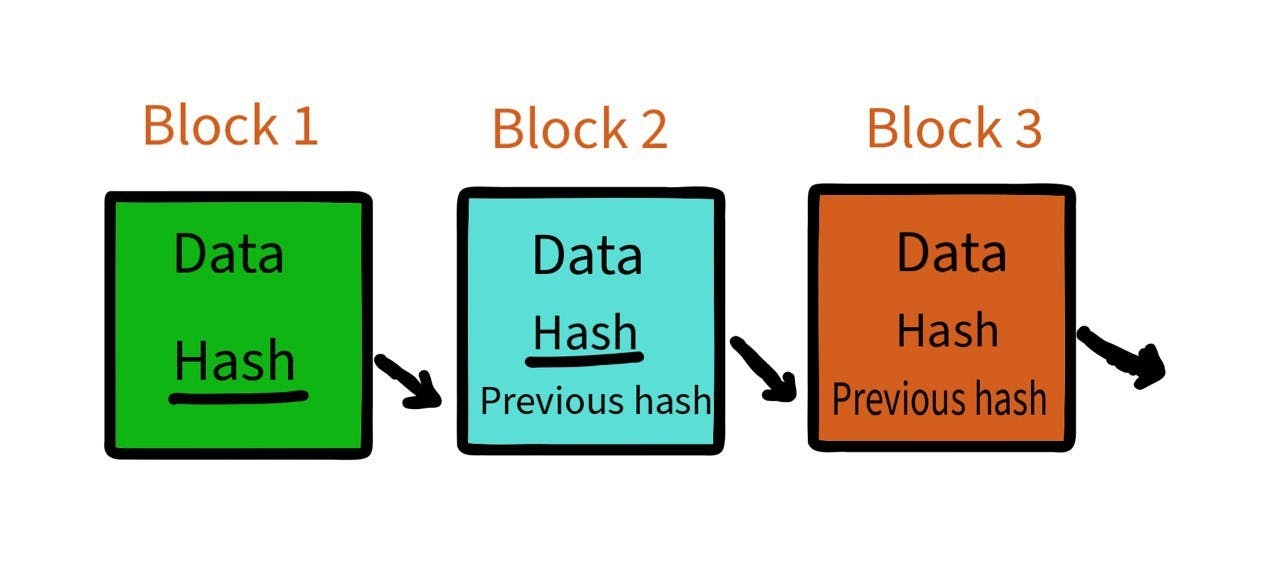
In Blockchain, hash of a block is generated by converting all the data it has into a hash output. This hash is stored in the next block. Even a slight change in a block's data will alter its hash and this change will be reflected in all the succeeding blocks linked to it. This makes the blockchain secure as any malicious attack will alter the information in all the blocks linked to the attacked one.
Timestamp : Timestamp indicates the time and date when the block was mined (included in the blockchain after validation).
Nonce : Nonce is basically a randomly generated number of size 4 bytes.
Every block's hash in a blockchain must meet the "difficulty level" requirements so that the block is considered valid. Since any change in the data (including transactions, timestamp, previous block's hash etc...) of the block changes its hash, nonce is the data field which miners play with to change the hash so that it meets the requirements. Why do they adjust nonce? Because practically, changing data in the transaction records till a valid hash is achieved will require a lot of time, energy and computational power coz there are unending combinations possible. Hence, nonce, having only 4 digits, is used for this purpose. The digits are adjusted till a desired hash is achieved.
Merkle Root : Merkle Root is the topic I will be covering in a separate blog but in basic language its the resultant hash of the hashing algorithm applied on all the data in a block. So, you can understand it as the hash of the current block.
I know there might be terms and concepts in this blog which are hard to grasp right now but don't worry at all, I will try my best to explain everything in the upcoming blogs.
I hope the content was useful and easy to understand.
That's all for today from my side. Thank You !! 😊😊
Credit : The main source of all this info is Consensys Academy tutorials

